Lien vers Basthon P5 : https://console.basthon.fr/
Mode écran avec p5
from p5 import *
from random import *
def setup():
createCanvas(600, 600)
background(20,20,20)
fill(10, 25, 10)
blendMode(SCREEN)
for x in range(30):
for n in range(1 + x):
rect(20 * x + randint(0,10), randint(-100,600), 80, 80)
def draw():
noLoop()
run()Mode multiplier – NUMWORKS
from kandinsky import *
from random import randint
def rvb01(c): return tuple(v / 255 for v in c)
def rvb255(c): return tuple(255 * v for v in c)
def zip01(c1,c2): return zip(rvb01(c1), rvb01(c2))
def multiply(c1,c2): return rvb255(a * b for (a, b) in zip01(c1,c2))
def rect(x,y,w,h,c,mode):
for i in range(w):
for j in range(h):
rvb = mode(c, get_pixel(x + i, y + j))
set_pixel(x + i, y + j, rvb)
for x in range(0,320,8):
for y in range(0,220,3):
rect(x + randint(0, 7), y + randint(0, 6), \
randint(1, 320 - x), randint(1, 9), (250, 100, 250), multiply)Mode différences – NUMWORKS et P5
# Version - NUMWORKS
from kandinsky import *
from random import *
def rvb01(c): return tuple(v / 255 for v in c)
def rvb255(c): return tuple(int(255 * v) for v in c)
def zip01(c1,c2): return zip(rvb01(c1),rvb01(c2))
def diff(c1,c2):
return rvb255(abs(a - b) for (a, b) in zip01(c1,c2))
def rect(x,y,w,h,c,mode):
for i in range(w):
for j in range(h):
rvb = mode(c, get_pixel(x + i, y + j))
set_pixel(x + i, y + j, rvb)
fill_rect(0,0,320,222,(250, 100, 250))
for _ in range(500):
t = randint(20,40)
rect(randint(-10, 315), randint(-10, 220), t, t, (250, 100, 250), diff)
# Version P5 - Python
from p5 import *
from random import *
c = (250, 100, 250)
def setup():
createCanvas(900, 600)
background(c)
blendMode(DIFFERENCE)
fill(c)
for _ in range(1000):
t = randint(20,80)
rect(randint(-20,900), randint(-20,600), t, t)
def draw():
noLoop()
run()Mode addition – NUMWORKS
from kandinsky import *
from random import *
from math import cos
def rvb01(c): return tuple(v / 255 for v in c)
def rvb255(c): return tuple(int(255 * v) for v in c)
def zip01(c1,c2): return zip(rvb01(c1),rvb01(c2))
def add(c1,c2):
return rvb255(min(1,a+b) for (a, b) in zip01(c1,c2))
def rect(x,y,w,h,c,mode):
for i in range(w):
for j in range(h):
rvb = mode(c, get_pixel(x + i, y + j))
set_pixel(x + i, y + j, rvb)
fill_rect(0,0,320,222,(40,40,40))
for i in range(50):
rect(randint(-20,300), randint(-20,200), 60, 60,\
(randint(0,255), randint(0,255), randint(0,255)), add)TISSU écossais – p5
Cet exemple a été supprimé au montage de la vidéo:
from p5 import *
def setup():
createCanvas(770, 770)
noStroke()
background((40,40,40))
blendMode(SCREEN)
fill(20, 40, 20)
for i in range(10):
for j in range(10):
rect(60 * i, 60 * j, 50 + 20 * i, 50 + 20 * j)
def draw():
noLoop()
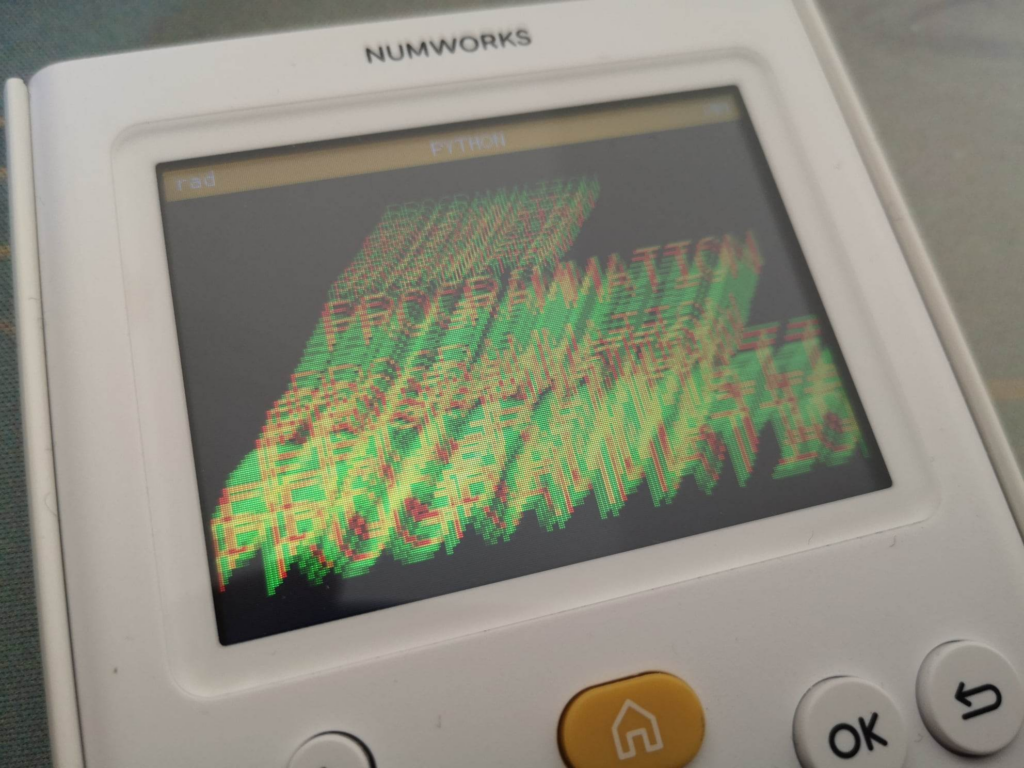
run()MODE addition – p5 et NUMWORKS
from p5 import *
from random import *
def setup():
createCanvas(800, 400)
noStroke()
background((50,50,50))
blendMode(ADD)
fill(20, 140, 20)
x, y = 200, 0
for i in range(100):
textSize(1 + i)
x -= 2
y += randint(-5,11)
fill(20, 140, 20)
if random()<.2: fill(255, 0, 0)
text('PROGRAMMATION', x, y)
def draw():
noLoop()
run()
from kandinsky import *
from random import *
BL, WH = (0, 0, 0), (255,) * 3
def rvb01(c): return tuple(v / 255 for v in c)
def rvb255(c): return tuple(int(255 * v) for v in c)
def zip01(c1,c2): return zip(rvb01(c1),rvb01(c2))
def screen(c1,c2):
return rvb255(1 - (1 - a) * (1 - b) for (a, b) in zip01(c1,c2))
def rect(x,y,w,h,c,mode):
for i in range(w):
for j in range(h):
rvb = mode(c, get_pixel(x + i, y + j))
set_pixel(x + i, y + j, rvb)
def dot(x, y, c, fg, t):
draw_string(c, 0, 0, fg, (0,0,0))
for v in range(18):
for u in range(9):
rect(x + u * t, y + v * t, t, t, get_pixel(u, v), screen)
def aff(txt, x, y, t):
coul = (255, 0, 0)if random()<.3 else (20, 140, 20)
for i, c in enumerate(txt):
dot(x + i * t * 9, y, c, coul, t)
fill_rect(0,0,320,222,(50,50,50))
x, y = 150, -30
for i in range(80):
x -= 2
y += randint(1,4)
aff("PROGRAMMATION", x, y, i//20)
fill_rect(0,0,20,20,(50,50,50))Dégradés – NUMWORKS
from kandinsky import *
def rvb01(c): return tuple(v / 255 for v in c)
def rvb255(c): return tuple(int(255 * v) for v in c)
def zip01(c1,c2): return zip(rvb01(c1),rvb01(c2))
def alpha(c1, t, c2):
return rvb255(a * t + b * (1 - t) for (a, b) in zip01(c1,c2))
def rect(x,y,w,h,c,d):
(dx,dy) = d
for i in range(w):
for j in range(h):
t = 1
if dx == 1: t = 1 - i / w
elif dx == -1: t = i / w
if dy == 1: t = 1 - j / h
elif dy == -1: t = j / h
rvb = alpha(c, t, get_pixel(x + i, y + j))
set_pixel(x + i, y + j, rvb)
rect(0, 0, 200, 200, (255, 0, 0), (1,0))
rect(0, 0, 200, 200, (0, 255, 0), (0,1))
rect(0, 0, 200, 200, (0, 0, 255), (-1,0))Effet alpha – NUMWORKS
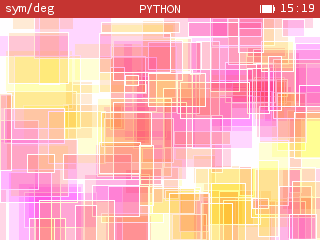
from kandinsky import *
from random import randint, choice
coul = (255,0,255), (255,255,0), (255,127,0), (255,0,127)
def rvb01(c): return tuple(v / 255 for v in c)
def rvb255(c): return tuple(int(255 * v) for v in c)
def zip01(c1,c2): return zip(rvb01(c1),rvb01(c2))
def alpha(c1, t, c2):
return rvb255(a * t + b * (1 - t) for (a, b) in zip01(c1,c2))
def rect(x,y,w,h,c,t):
for i in range(w):
for j in range(h):
if i == 0 or j == 0 or i == w - 1 or j == h - 1:
rvb = (255,255,255)
else:
rvb = alpha(c, t, get_pixel(x + i, y + j))
set_pixel(x + i, y + j, rvb)
def effet(t):
for _ in range(150):
x, y = randint(-10,300), randint(-10,200)
w, h = randint(10,80), randint(10,80)
rect(x,y,w,h,choice(coul),t)
effet(0.15)